2. AP计算机2015年考试:多项选择
Consider the following incomplete method, which is intended to return the number of integers that evenly divide the integer inputVal. Assume that inputVal is greater than 0.
public static int numDivisors(int inputVal)
{
int count = 0;
for (int k = 1; k <=inputVal; k++)
{
if ( /* condition */ )
{
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
Which of the following can be used to replace /* condition */ so that numDivisors will work as intended?
inputVal % k == 0
k % inputVal == 0
inputVal % k != 0
inputVal / k == 0
k / inputVal > 0
Consider the following code segment.
for (int r = 3; r > 0; r--)
{
int c;
for (c = 1; c < r; c++)
{
System.out.print("-");
}
for (c = r; c <= 3; c++)
{
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
What is printed as a result of executing the code segment?
--* -** ***
*-- **- ***
*** -** --*
*** **- *--
--* *** --*
Consider the following two classes.
public class A
{
public void show()
{
System.out.print("A");
}
}
public class B extends A
{
public void show()
{
System.out.print("B");
}
}
What is printed as a result of executing the following code segment?
A obj = new B();
obj.show();
A
B
AB
BA
The code results in a runtime error.
Consider the following instance variable and method.
private int[] arr;
/** Precondition: arr.length > 0
* @return the largest value in array arr
*/
public int findMax()
{
int maxVal = 0;
for (int val : arr)
{
if (val > maxVal)
{
maxVal = val;
}
}
return maxVal;
}
Method findMax is intended to return the largest value in the array arr. Which of the following best describes the conditions under which the method findMax will not work as intended?
The largest value in arr occurs only once and is in arr[0].
The largest value in arr occurs only once and is in arr[arr.length - 1].
The largest value in arr is negative.
The largest value in arr is zero.
The largest value in arr occurs more than once.
Assume that x and y are boolean variables and have been properly initialized.
(x || y) && x
Which of the following always evaluates to the same value as the expression above?
x
y
x && y
x || y
x != y
Consider the following method, which is intended to return true if at least one of the three strings s1, s2, or s3 contains the substring art. Otherwise, the method should return false.
public static boolean containsArt(String s1, String s2, String s3)
{
String all = s1 + s2 + s3;
return (all.indexOf("art") != -1);
}
Which of the following method calls demonstrates that the method does not work as intended?
containsArt("rattrap", "similar", "today")
containsArt("start", "article", "Bart")
containsArt("harm", "chortle", "crowbar")
containsArt("matriculate", "carat", "arbitrary")
containsArt("darkroom", "cartoon", "articulate")
Consider the following code segment.
for (int outer = 1; outer <= 6; outer ++)
{
for (int inner = outer; inner <=6; inner ++)
{
if (inner % 2 == 0)
{
System.out.print(inner + " ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
What will be printed as a result of executing the code segment?
2 4 6
4 6
6
2 4 6
2 4 6
2 4 6
2 4 6
2 4 6
4 6
4 6
6
6
2 4 6
2 4 6
2 4 6
2 4 6
2 4 6
2 4 6
2 4
2 4
4
4
Consider the following method.
public static int[] operation(int[][] matrix, int r, int c)
{
int[] result = new int[matrix.length];
for (int j = 0; j < matrix.length; j++)
{
result[j] = matrix[r][j] * matrix[j][c];
}
return result;
}
The following code segment appears in another method in the same class.
int[][] mat = { {3, 2, 1, 4},
{1, 2, 3, 4},
{2, 2, 1, 3},
{1, 1, 1, 1} };
int[] arr = operation(mat, 1, 2);
Which of the following represents the contents of arr as a result of executing the code segment?
{6, 4, 2, 4}
{1, 6, 3, 4}
{4, 3, 6, 1}
{4, 4, 2, 2}
{2, 2, 4, 4}
A pair of number cubes is used in a game of chance. Each number cube has six sides, numbered from 1 to 6, inclusive, and there is an equal probability for each of the numbers to appear on the top side (indicating the cube’s value) when the number cube is rolled. The following incomplete statement appears in a program that computes the sum of the values produced by rolling two number cubes.
int sum = /* missing code */;
Which of the following replacements for /* missing code */ would best simulate the value produced as a result of rolling two number cubes?
2 * (int) (Math.random() * 6)
2 * (int) (Math.random() * 7)
(int) (Math.random() * 6) + (int) (Math.random() * 6)
(int) (Math.random() * 13)
2 + (int) (Math.random() * 6) + (int) (Math.random() * 6)
Consider the following interface and class declarations.
public interface Student
{ /* implementation not shown */ }
public class Athlete
{ /* implementation not shown */ }
public class TennisPlayer extends Athlete implements Student
{ /* implementation not shown */ }
Assume that each class has a zero-parameter constructor. Which of the following is not a valid declaration?
Student a = new TennisPlayer()
TennisPlayer b = new TennisPlayer()
Athlete c = new TennisPlayer()
Student d = new Athlete();
Athlete e = new Athlete();
Consider the following method.
public static boolean mystery(String str)
{
String temp = "";
for (int k = str.length(); k > 0; k--)
{
temp = temp + str.substring(k - 1, k);
}
return temp.equals(str);
}
Which of the following calls to mystery will return true?
mystery("no")
mystery("on")
mystery("nnoo")
mystery("nono")
mystery("noon")
Assume that x and y are boolean variables and have been properly initialized.
(x && y) && !(x || y)
Which of the following best describes the result of evaluating the expression above?
true always
false always
true only when x is true and y is true
true only when x and y have the same value
true only when x and y have different values
Consider the following instance variable and method.
private int[] numbers;
public void mystery(int x)
{
for (int k = 1; k < numbers.length; k = k + x)
{
numbers[k] = numbers[k - 1] + x;
}
}
Assume that numbers has been initialized with the following values.
{17, 34, 21, 42, 15, 69, 48, 25, 39}
Which of the following represents the order of the values in numbers as a result of the call mystery(3)?
{17, 20, 21, 42, 45, 69, 48, 51, 39}
{17, 20, 23, 26, 29, 32, 35, 38, 41}
{17, 37, 21, 42, 18, 69, 48, 28, 39}
{20, 23, 21, 42, 45, 69, 51, 54, 39}
{20, 34, 21, 45, 15, 69, 51, 25, 39}
Consider the following method, biggest, which is intended to return the greatest of three integers. It does not always work as intended.
public static int biggest(int a, int b, int c)
{
if ((a > b) && (a > c))
{
return a;
}
else if ((b > a) && (b > c))
{
return b;
}
else
{
return c;
}
}
Which of the following best describes the error in the method?
biggest always returns the value of a.
biggest may not work correctly when c has the greatest value.
biggest may not work correctly when a and b have equal values.
biggest may not work correctly when a and c have equal values.
biggest may not work correctly when b and c have equal values.
Consider the following method.
public static void showMe(int arg)
{
if (arg < 10)
{
showMe(arg+1);
}
else
{
System.out.print(arg + " ");
}
}
What will be printed as a result of the call showMe(0)?
10
11
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Consider the following method.
/** Precondition: values has at least one row */
public static int calculate(int [][] values)
{
int found = values[0][0];
int result = 0;
for (int[] row : values)
{
for (int y = 0; y < row.length; y++)
{
if (row[y] > found)
{
found = row[y];
result = y;
}
}
}
return result;
}
Which of the following best describes what is returned by the calculate method?
The largest value in the two-dimensional array
The smallest value in the two-dimensional array
The row index of an element with the largest value in the two-dimensional array
The row index of an element with the smallest value in the two-dimensional array
The column index of an element with the largest value in the two-dimensional array
Consider the following method.
/** Precondition: num > 0 */
public static int doWhat(int num)
{
int var = 0;
for (int loop = 1; loop <= num; loop = loop + 2)
{
var += loop;
}
return var;
}
Which of the following best describes the value returned from a call to doWhat?
num
The sum of all integers between 1 and num, inclusive
The sum of all even integers between 1 and num, inclusive
The sum of all odd integers between 1 and num, inclusive
No value is returned because of an infinite loop.
What is printed as a result of executing the following statement?
System.out.println(404 / 10 * 10 + 1);
4
5
41
401
405
Consider the following code segment.
int x = 1;
while ( /* condition */ )
{
if (x % 2 == 0)
{
System.out.print(x + " ");
}
x = x + 2;
}
The following conditions have been proposed to replace /* condition /* in the code segment.
I. x<0
II. x<=1
III. x<10
For which of the conditions will nothing be printed?
I only
II only
I and II only
I and III only
I, II, and III
Consider the following method.
/** Precondition: arr.length > 0 */
public static int mystery(int[] arr)
{
int index = 0;
int count = 0;
int m = -1;
for (int outer = 0; outer < arr.length; outer++)
{
count = 0;
for (int inner = outer + 1; inner < arr.length; inner++)
{
if (arr[outer] == arr[inner])
{
count++;
}
}
if (count > m)
{
index = outer;
m = count;
}
}
return index;
}
Assume that nums has been declared and initialized as an array of integer values. Which of the following best describes the value returned by the call mystery(nums)?
The maximum value that occurs in nums
An index of the maximum value that occurs in nums
The numbers of times that the maximum value occurs in nums
A value that occurs most often in nums
An index of a value that occurs most often in nums
Consider the following recursive method.
public static void whatsItDo(String str)
{
int len = str.length();
if (len > 1)
{
String temp = str.substring(0, len - 1);
System.out.println(temp);
whatsItDo(temp);
}
}
What is printed as a result of the call whatsItDo("WATCH")?
H
WATC
ATCH
ATC
AT
A
WATC
WAT
WA
W
WATCH
WATC
WAT
WA
Consider the following definition.
int[][] numbers = { {1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6} };
Which of the following code segments produces the output 123456?
for (int[] row : numbers)
{
for (int n : row)
{
System.out.print(n);
}
}
for (int[] row : numbers)
{
for (int n : row)
{
System.out.print(row[n]);
}
}
for (int rc = 0; rc < numbers.length; rc++)
{
System.out.print(numbers[rc]);
}
for (int r = 0; r < numbers[0].length; r++)
{
for (int c = 0; c < numbers.length; c++)
{
System.out.print(numbers[r][c]);
}
}
for (int c = 0; r < numbers[0].length; r++)
{
for (int r = 0; c < numbers.length; c++)
{
System.out.print(numbers[r][c]);
}
}
Consider the following code segment from an insertion sort program.
for (int j = 1; j < arr.length; j++)
{
int insertItem = arr[j];
int k = j - 1;
while(k >= 0 && insertItem < arr[k])
{
arr[k+1] = arr[k];
k--;
}
arr[k + 1] = insertItem;
/* end of for loop */
}
Assume that array arr has been defined and initialized with the values {5, 4, 3, 2, 1}. What are the values in array arr after two passes of the for loop(i.e., when j = 2 at the point indicated by /* end of for loop */)?
{2, 3, 4, 5, 1}
{3, 2, 1, 4, 5}
{3, 4, 5, 2, 1}
{3, 5, 2, 3, 1}
{5, 3, 4, 2, 1}
Consider the following class.
public class SomeMethods
{
public void one(int first)
{ /* implementation not shown */ }
public void one(int first, int second)
{ /* implementation not shown */ }
public void one(int first, String second)
{ /* implementation not shown */ }
}
Which of the following methods can be added to the SomeMethods class without causing a compile-time error?
I. public void one(int value)
II. public void one(String first, int second)
III. public void one(int first, int second, int thrid)
I only
I and II only
I and III only
II and III only
I, II, and III
Consider the following code segment.
int count = 0;
for (int x = 0; x < 4; x++)
{
for (int y = x; y < 4; y++)
{
count++;
}
}
System.out.println(count);
What is printed as a result of executing the code segment.
4
8
10
16
20
Consider the following two methods, which appear within a single class.
public static void changeIt(int[] arr, int val, String word)
{
arr = new int[5];
val = 0;
word = word.substring(0, 5);
for (int k = 0; k < arr.length; k++)
{
arr[k] = 0;
}
}
public static void start()
{
int[] nums = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int value = 6;
String name = "blackboard";
changeIt(nums, value, name);
for (int k = 0; k < nums.length; k++)
{
System.out.print(nums[k]+ " ");
}
System.out.print(value + " ");
System.out.print(name);
}
What is printed as a result of the call start()?
0 0 0 0 0 0 black
0 0 0 0 0 6 blackboard
1 2 3 4 5 6 black
1 2 3 4 5 0 black
1 2 3 4 5 6 blackboard
Consider the following sort method. This method correctly sorts the elements of array data into increasing order.
public static void sort(int[] data)
{
for (int j = 0; j < data.length - 1; j++)
{
int m = j;
for (int k = j + 1; k < data.length; k++)
{
if (data[k] < data [m]) /* Compare values */
{
m = k;
}
}
int temp = data[m]; /* Assign to temp */
data[m] = data[j];
data[j] = temp;
/* End of outer loop */
}
}
Assume that sort is called with the array {6 ,3, 2, 5, 4, 1}. What will the value of data be after three passes of the outer loop (i.e., when j = 2 at the point indicated by /* End of outer loop */)?
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
{1, 2, 3, 5, 4, 6}
{1, 2, 3, 6, 5, 4}
{1, 3, 2, 4, 5, 6}
{1, 3, 2, 5, 4, 6}
Assume that sort is called with the array {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}. How many times will the expression indicated by /* Compare value */ and the statement indicated by /* Assign to temp */ execute?
15 0
15 5
15 6
21 5
21 6
Consider the following recursive method.
/** Precondition: num>=0 */
public static int what(int num)
{
if (num > 10)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 1 + what(num / 10);
}
}
Assume that int val has been declared and initialized with a value that satisfies the precondition of the method. Which of the following best describes the value returned by the call what(val)?
The number of digits in the decimal representation of val is returned.
The sum of the digits in the decimal representation of val is returned.
Nothing is returned. A run-time error occurs because of infinite recursion.
The value 1 is returned.
The value val/10 is returned.
The price per box of ink pens advertised in an office supply catalog is based on the number of boxes ordered. The following table shows the pricing.
| Number of Boxes | Price per Box |
|---|---|
| 1 up to but not including 5 | $5.00 |
| 5 up to but not including 10 | $3.00 |
| 10 or more | $1.50 |
The following incomplete method is intended to return the total cost of an order based on the value of the parameter numBoxes.
/** Precondition: numBoxes>0 */
public static double getCost(int numBoxes)
{
double totalCost = 0.0;
/* missing code */
return totalCost;
}
Which of the following code segments can be used to replace /* missing code */ so that method getCost will work as intended?
I.
if (numBoxes >= 10)
{
totalCost = numBoxes * 1.50;
}
if (numBoxes >= 5)
{
totalCost = numBoxes * 3.00;
}
if (numBoxes > 0)
{
totalCost = numBoxes * 5.00;
}
II.
if (numBoxes >= 10)
{
totalCost = numBoxes * 1.50;
}
else if (numBoxes >= 5)
{
totalCost = numBoxes * 3.00;
}
else
{
totalCost = numBoxes * 5.00;
}
III.
if (numBoxes > 0)
{
totalCost = numBoxes * 5.00;
}
else if (numBoxes >= 5)
{
totalCost = numBoxes * 3.00;
}
else if (numBoxes >= 10)
{
totalCost = numBoxes * 1.50;
}
I only
II only
III only
I and II
II and III
Consider the following code segment.
String[][] board = new String[5][5];
for (int row = 0; raw < 5; row++)
{
for (int col = 0; col < 5; col++)
{
board[row][col] = "O";
}
}
for (int val = 0; val < 5; val++)
{
if (val % 2 == 1)
{
int row = val;
int col = 0;
while (col < 5 && row >= 0)
{
board[row][col] = "X";
col++;
row--;
}
}
}
Which of the following represents board after this code segment is executed?
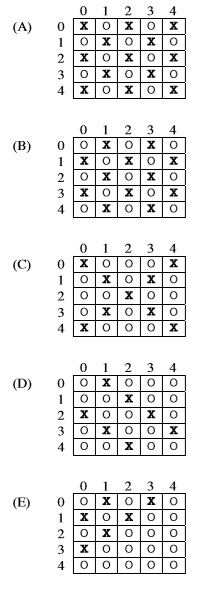
A
B
C
D
E
Consider the following class declaration.
public class StudentInfo
{
private String major;
private int age;
public String getMajor()
{ return major; }
public String getAge()
{ return age; }
// There may be instance variables, constructors, and methods that are not shown.
}
The following instance variable and method appear in another class.
private List students;
/** @return the average age of students with the given major;
* -1.0 if no such students exist
*/
public double averageAgeinMajor(String theMajor)
{
double sum = 0.0;
int count = 0;
for (StudentInfo k : students)
{
/* missing code */
}
if (count > 0)
{
return sum / count;
}
else
{
return -1.0;
}
}
Which of the following could be used to replace /* missing code */ so that averageAgeInMajor will compile without error?
if (theMajor.equals(k.major))
{
sum += k.age;
count++
}
if (theMajor.equals(k.getMajor()))
{
sum += k.getAge();
count++
}
if (theMajor.equals(k.major))
{
sum += k.getAge();
count++
}
if (theMajor.equals(students[k].getMajor()))
{
sum += students[k].getAge();
count++
}
if (theMajor.equals(getMajor(k)))
{
sum += getAge(k);
count++
}
Which of the following statements regarding interfaces is FALSE?
All methods in an interface are public.
An interface cannot be instantiated.
An interface can declare an instance variable.
A non-abstract class can implement an interface.
An abstract class can implement an interface.
Consider the problem of finding the maximum value in an array of integers. The following code segments are proposed solutions to the problem. Assume that the variable arr has been defined as an array of int values and has been initialized with one or more values.
I.
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int value : arr)
{
if (max < value)
{
max = value;
}
}
II.
int max = 0;
boolean first = true;
for (int value : arr)
{
if (first)
{
max = value;
first = false;
}
else if (max < value)
{
max = value;
}
}
III.
int max = arr[0];
for (int k = 1; k < arr.length; k++)
{
if (max < arr[k])
{
max = arr[k];
}
}
Which of the code segments will always correctly assign the maximum element of the array to the variable max?
I only
II only
III only
II and III only
I, II, and III
Consider the following instance variable and method. Method wordsWithCommas is intended to return a string containing all the words in listOfWords contains ["one", "two", "three"], the string returned by the call wordsWithCommas() should be "{one, two, three}".
private List listOfWords;
public String wordsWithCommas()
{
String result = "{";
int sizeOfList = /* expression */;
for (int k=0; k < sizeOfList; k++)
{
result = result + listOfWords.get(k);
if ( /* condition */ )
{
result = result + ", ";
}
}
result = result + "}";
return result;
}
Which of the following can be used to replace /* expression */ and /* condition */ so that wordsWithCommas will work as intended?
listOfWords.size() - 1 k != 0
listOfWords.size() k != 0
listOfWords.size() - 1 k != sizeOfList - 1
listOfWords.size() k != sizeOfList - 1
result.length() k != 0
Consider the following binarySearch method. The method correctly performs a binary search.
/** Precondition: data is sorted in increasing order. */
public static int binarySearch(int[] data, int target)
{
int start = 0;
int end = data.length - 1;
while (start <= end)
{
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (target data[mid])
{
start = mid + 1;
}
else
{
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
Consider the following code segment.
int[] values = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 8, 8};int target = 8;
What value is returned by the call binarySearch(values, target)?
-1
3
5
6
8
Suppose the binarySearch method is called with an array containing 2,000 elements sorted in increasing order. What is the maximum number of times that the statement indicated by /* Calculated midpoint */ could execute?
2,000
1,000
20
11
1
Consider the following incomplete method that is intended to return a string formed by concatenating elements from the parameter words. The elements to be concatenated start with startIndex and continue through the last element of words and should appear in reverse order in the resulting string.
/** Precondition: words. length > 0;
* startIndex >= 0
*/
public static String concatWords(String[] words, int startIndex)
{
String result = "";
/* missing code */
return result;
}
For example, the following code segment uses a call to the concatWords method.
String[] things = {"Bear, "Apple", "Gorilla", "House", "Car"};System.out.println(concatWords(things, 2));
When the code segment is executed, the string "CarHouseGorilla" is printed.
The following three code segments have been proposed as replacements for /* missing code */.
I.
for (int k = startIndex; k < words.length; k++)
{
result += words[k] + words[words.length - k - 1];
}
II.
int k = words.length - 1;
while (k >= startIndex)
{
result += words[k];
k--;
}
III.
String[] temp = new String[words.length];
for (int k = 0; k <= words.length / 2; k++)
{
temp[k] = words[words.length - k - 1];
temp[words.length - k - 1] = words[k];
}
for (int k = 0; k < temp.length - startIndex; k++)
{
result += temp[k];
}
Which of these code segments can be used to replace /* missing code */ so that concatWords will work as intended?
I only
II only
III only
I and II
II and III
Consider the following method.
/** Precondition: 0 < numVals <= nums.length */
public static int mystery(int[] nums, int v, int numVals)
{
int k = 0;
if (v == nums[numVals - 1])
{
k = 1;
}
if (numVals == 1)
{
return k;
}
else
{
return k + mystery(nums, v, numVals - 1);
}
}
Which of the following best describes what the call mystery(numbers, val, number.length) does? You may assume that variables numbers and val have been declared and initialized.
Returns 1 if the last element in numbers is equal to val; otherwise, returns 0
Returns the index of the last element in numbers that is equal to val
Returns the number of elements in numbers that are equal to val
Returns the number of elements in numbers that are not equal to val
Returns the maximum number of adjacent elements that are not equal to val
Consider the following code segment.
List students = new ArrayList();
students.add("Alex");
students.add("Bob");
students.add("Carl");
for (int k = 0; k < students.size(); k++)
{
System.out.print(students.set(k, "Alex") + " ");
}
System.out.println();
for (String str : students)
{
System.out.print(str + " ");
}
What is printed as a result of executing the code segment?
Alex Alex Alex Alex Alex Alex
Alex Alex Alex Alex Bob Carl
Alex Bob Carl Alex Alex Alex
Alex Bob Carl Alex Bob Carl
Nothing is printed because the first print statement will cause a runtime exception to be thrown.